life@seasontwo.com
Evolution from Old Age Homes to Senior Living Communities

Introduction
Ageing is an inevitable part of life, bringing physical and mental changes that often require specialized care. As people grow older, they may face health challenges such as arthritis, diabetes, hypertension, and cognitive conditions like Alzheimer’s and dementia. Beyond physical care, emotional support is equally critical, as loneliness and depression can significantly impact seniors’ well-being. Providing the right balance of health assistance and companionship is essential for older adults to lead fulfilling lives. Over time, elder care has evolved significantly, transitioning from traditional family-based care to old age homes and, more recently, to modern senior living communities that offer a holistic and dignified lifestyle.
Traditional Family-Based Elder Care
Historically, caring for the elderly was a family responsibility, particularly for children. In joint family systems, where multiple generations lived together, caregiving duties were shared among family members, ensuring seniors’ needs were met effectively. This model thrived in societies where extended families were the norm, providing a supportive environment for older adults.
However, societal changes, such as urbanization and the rise of nuclear families, disrupted this traditional model. With smaller households- typically consisting of four to six members- families faced challenges balancing personal lives, careers, and the demands of elder care. This shift highlighted the need for alternative solutions to support ageing populations effectively.
The Rise of Old Age Homes
As traditional caregiving became less feasible, old-age homes emerged as a practical alternative. These facilities offered essential services, including medical care, daily assistance, and safe living environments for seniors. For many families, old age homes provided a way to ensure their loved ones received proper care while managing their own responsibilities.
Despite their benefits, old age homes faced mixed societal reactions. Some viewed them as a sign of abandonment, with a stigma that sending parents to such facilities was disrespectful. In reality, many old age homes were equipped with resources and expertise difficult to replicate at home, fostering supportive environments for seniors. However, negative perceptions often overshadowed these advantages, creating a societal taboo around the concept.
Redefining Elder Care
Over time, increased awareness and understanding of elder care benefits led to a shift in societal attitudes. The stigma surrounding old age homes stemmed from a misunderstanding of their purpose. Far from being places of abandonment, these facilities were designed to provide personalised, round-the-clock care in a community setting that promoted health and happiness. This shift in perception paved the way for a redefinition of elder care, with traditional old age homes evolving into what are now known as modern senior living communities. These modern communities focus on creating a “home away from home,” emphasizing dignity, independence, and well-being.
Social and Cultural Drivers of Change
Several factors have contributed to the growing acceptance of senior living communities. Increased migration has led to geographically dispersed families, making it harder to provide hands-on care for elderly relatives. Improved literacy rates have raised awareness about the benefits of specialized care environments. Additionally, there is a growing demand for quality living spaces that cater to seniors’ unique needs.
Research suggests that the desire for supportive communities, access to quality healthcare, and opportunities for social interaction are significant drivers of this trend, Unlike old age homes, which were often criticized for lacking warmth, senior living communities are designed to offer a holistic lifestyle, including luxury amenities, healthcare services, and recreational activities. This evolution has transformed societal perceptions, moving from stigma to viewing these communities as aspirational and dignified living options.
Seniors Embracing Active and Purposeful Living
Today, many seniors proactively choose senior living communities, recognizing their benefits. Unlike the traditional view of old age as a time for slowing down, often associated with passive activities like pilgrimages or spending time with grandchildren, modern seniors see their later years as an opportunity to live life on their terms. Financially stable and socially engaged, these individuals seek environments that align with their vision for their silver years.
Senior living communities cater to this mindset by offering both independent and assisted living options, 24/7 healthcare, and emergency services. These communities allow family members to focus on their careers and personal lives with peace of mind, knowing their loved ones are in a safe and vibrant environment.
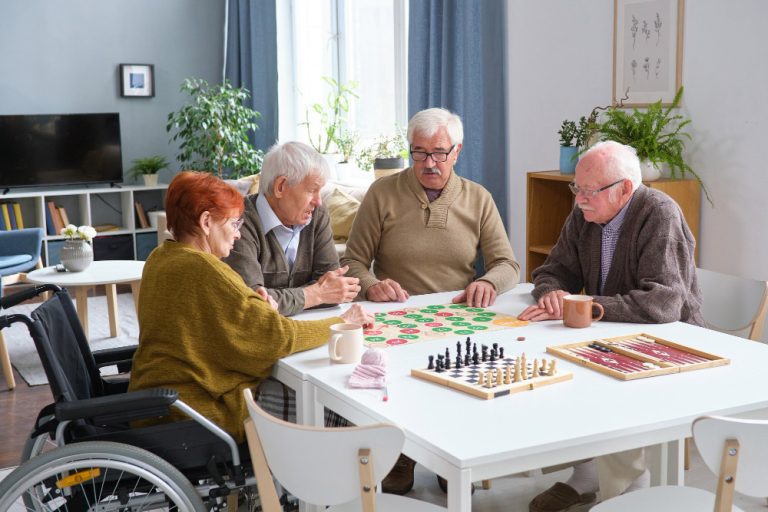
Key Features of Senior Living Communities
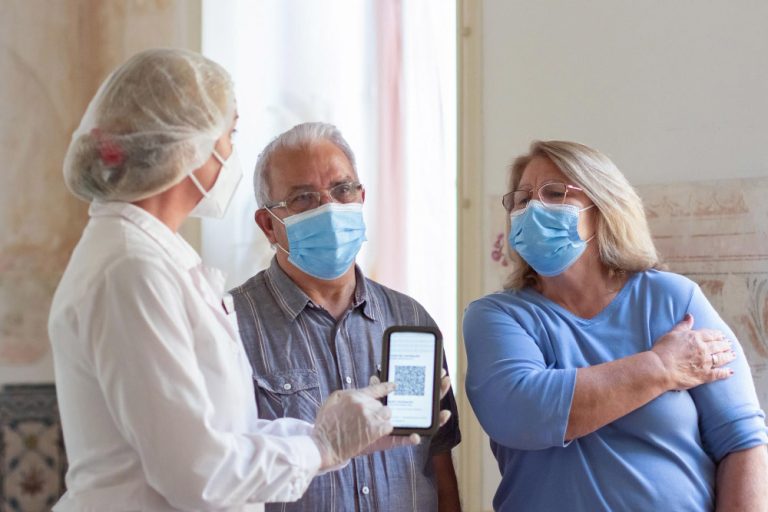
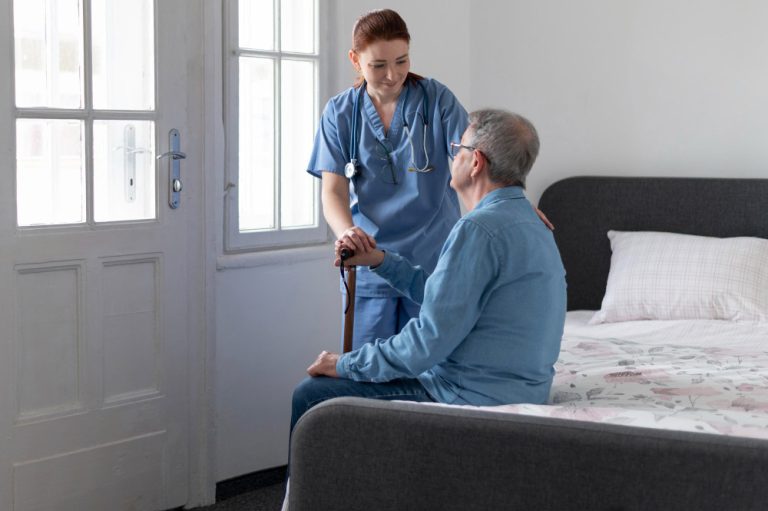
Senior living communities are thoughtfully designed to cater to the unique needs of older adults, offering a well-rounded and supportive environment. One of the standout features is the availability of round-the-clock healthcare services, ensuring that both physical and cognitive health needs are promptly and professionally addressed. These communities also place a strong emphasis on social engagement by organising various activities such as group outings, hobby clubs, and community events, which help residents stay socially connected and emotionally fulfilled. The physical layout of these spaces prioritises accessibility and safety, incorporating features like handrails, non-slip surfaces, and ramps to accommodate mobility needs. Additionally, residents can chooseliving options based on their requirements. This blend of care, comfort, and community creates a nurturing space where seniors can enjoy a dignified and enriching lifestyle
A Global Call for Compassionate Care
The global population is ageing rapidly, with significant implications for elder care. According to the World Health Organization, by 2030, 1 in 6 people worldwide will be aged 60 or older, a significant increase from current numbers. This demographic shift, driven by rising life expectancy and declining fertility rates, underscores the need for innovative care solutions. Senior living communities are well-positioned to address these challenges, offering environments that support healthy ageing and enhance quality of life.
Embracing senior living communities is not just a practical choice but a compassionate one, reflecting a commitment to ensuring older adults live with dignity and purpose. As the global ageing population grows, these communities will play an increasingly vital role in meeting the needs of seniors worldwide.
Conclusion The evolution from old age homes to senior living communities marks a significant shift in how society approaches elder care. Driven by changing social dynamics, increased awareness, and a desire for a better quality of life, this transition highlights the importance of compassionate and comprehensive care for seniors. As the global population continues to age, senior living communities will remain essential, ensuring older adults can live happily, healthily, and independently in environments that prioritize their well-being.